¶ Kafka SASL ACL Management
The CTO2B platform uses a kafka-gitops-based ACL (Access Control List) management model to efficiently manage permissions and access controls within the system.
The CTO2B Kafka-GitOps operator (Figure 1) serves as the central management tool for administering these ACLs. The operator interacts with both Kafka and GitOps tools to automate and enforce access policies. With this operator, administrators can seamlessly apply access rules defined in Git repositories, ensuring that any changes to ACLs are tracked, versioned, and auditable.
Figure 1. High level implementation architecture
The integration with GitOps allows for the following:
-
Declarative Configuration: ACLs are stored in Git repositories, ensuring that the configuration is always up to date and can be easily rolled back to previous versions if needed.
-
Automation & Consistency: The operator automatically applies any changes made to the ACL configurations, eliminating manual errors and ensuring consistent access control management across the Kafka ecosystem.
-
Auditability: All changes to the ACLs are tracked via Git, allowing for detailed audit logs and an overview of who made specific changes at any point in time.
-
Scalability & Flexibility: As Kafka clusters grow or change, the GitOps-driven approach scales seamlessly, allowing for effortless updates and reconfiguration without downtime or disruption to services.
¶ Overview of KACL Flow
Kafka Access Control Lists (KACL) define permissions for users accessing Kafka resources using SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer) authentication. This process involves creating Kafka users, configuring ACLs, and managing authentication/authorization at different levels.
Below, we break down Figure 1.1 into detailed steps.
Figure 1.1 Kacl deployment resource creation tree
Kafka users must be authenticated using SASL, which requires defining users and securely storing their credentials.
ACLs (Access Control Lists) define the authorization policies for Kafka users, specifying what actions they can perform on Kafka resources.
Kacl can be deployed as separate deployment or as dependency bundle with application deployment (Figure 2)
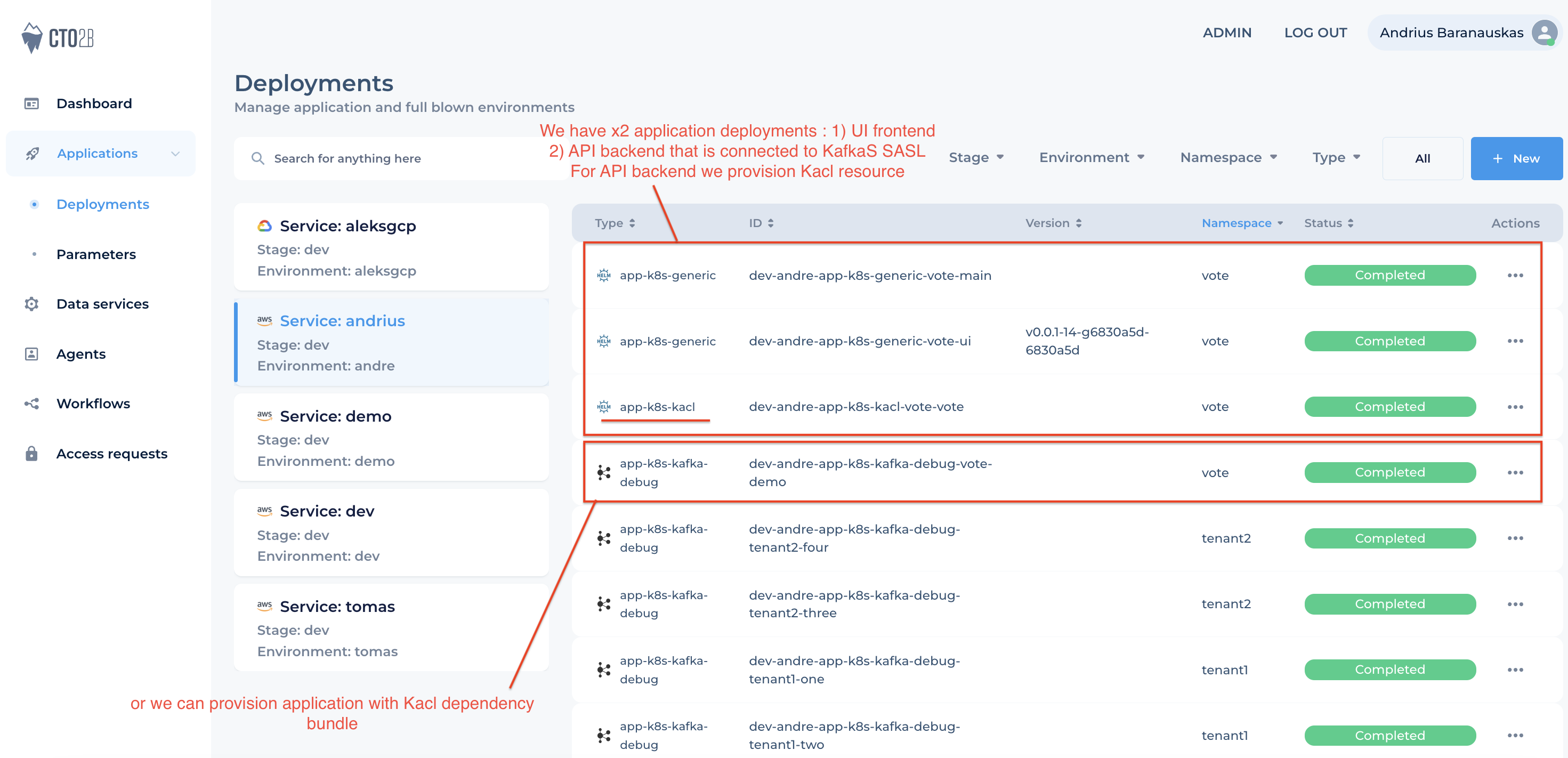
Figure 2. Deployment Options
¶ Kacl values
Lets drill down in to dev-andre-app-k8s-kacl-vote-vote example Kacl deployment values (Table 1)
NOTE: you username will be
<stage>-vote-api-user, all topics will apend<stage>.vote.api.<topic name in kacl>.
belongsTo: shared
cluster: kafka-bootstrap.kafka.svc.cluster.local
tenant: vote
# capability user name in full username vote-api-user
user: api
consumerGroups: []
idempotent: false
acls: {}
# - topic: api.commands.
# role: multiwriter
# user: core
global: {}
metadata: {}
| kacl values | Table 1 |
|---|---|
belongsTo: |
its kafka instance name you have deployed. |
cluster: |
kafka cluster bootstrap service name. It never change if you deploy from CTO2B catalog. just namespace matters kafka-bootstrap.<namespace>.svc.cluster.local instance name auto added full cluster expected in current example kafka-shared-kafka-bootstrap.kafka.svc.cluster.local |
tenant: |
tenant name where tenant will be auto added to etch topic policy and kafka user. usaly tenant = namespace |
user: |
capability/application user name. full user looks like <tenant>-<user>-user. In this example username would be vote-api-user Is part of ACL policy |
idempotent: |
enable IdempotentWrite and TransactionalDescribe for cluster resource if needed |
acls: [optional] |
custom additional ACL's for other users. In this example vote-api-user getting all privileges on topics starting with <stage>.<tenant>.<user>. like dev.vote.api.* and same for consumer group dev.vote.api.*, but if we like to grant another application to access some topic like dev.vote.api.events we need define it in acls: |
topic: |
part of acls: require to define topic in LITERAL (dev.vote.api.events) or PREFIX (dev.vote.api.) way. NOTE: <stage>.<tenant>. not need to be defined in topic: name |
role: |
role definition refer for selection to (Table 2) |
acls.user: |
user you grant access to your capability topic you manage |
global |
defining acls: as global if we join with application deployment |
metadata |
system value to pass stage, environment, cloud and other system vars. usualy --> Do not modify! <-- |
¶ Kacl access roles
simple roles that we define as additional custom ACL for another user which is not part of this Kacl
| Kacl roles | | Table 2 |
| Role | Rights | Description |
|---|---|---|
reader |
READ |
only LITERAL to specific topic read |
multireader |
READ |
to PREFIXed topics read all aftersome. |
writer |
WRITE |
only LITERAL to specific topic write. Write allow read as well |
multiwriter |
WRITE |
to PREFIXed topics write to all aftersome. Write allow read as well |
admin |
ALL |
only LITERAL to specific topic admin |
multiadmin |
ALL |
to PREFIXed topics all rights aftersome. |
¶ Consumer Groups
Each KACL or called service user (“owner”) to have their own consumer groups under ...anyconsumergroup (this is the default and intended design). Any other services that need to cross-join can be granted access to those accounts using the consumerGroup setting.
belongsTo: shared
cluster: kafka-bootstrap.kafka.svc.cluster.local
tenant: vote
user: api
consumerGroups:
- name: test2.
idempotent: false
acls: {}
As per example you grant <stage>-vote-api-user to join consumer group <stage>.vote.test2.*
¶ TLS Certificates
In Kubernetes environments that use cert-manager, certificates should be managed separately from other resources like Kacl.
Instead of embedding the TLS certificate within the Kacl resource, it should be deployed independently using the cert-manager Certificate API: Certificate apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1.
¶ Example use
Voting application tenant (Figure 3) where we have UI, API and Bootstrap demo app pods. Bootstrap application uses demo user and creates and controlls all topics required for API application. This allow us to clone vote tenant and ensure multi-tenancy in shared kafka cluster.
Figure 3. Voting tenant architecture
In demo debug application deployment Chart.yaml we link kacl chart
apiVersion: v2
name: kafka-debug
description: Kafka Debug
version: 0.1.0
dependencies:
- name: kacl
version: 0.1.0
repository: "file://../app-k8s-kacl/"
Then update default values by adding kacl: part. This required just once
Values
¶ Debug demo app chart
- Update values for debug demo app
- Add kacl default values
- update kacl values
- define topics you will create and manage
- define demo user and custom ACLs for api user
- update kacl values
¶ Some Code
resources:
limits:
memory: "1024Mi"
cpu: 1500m
requests:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: 100m
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: cloud.google.com/gke-nodepool
operator: In
values:
- pool
- matchExpressions:
- key: pool-type
operator: In
values:
- main
enVars:
- name: KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS
value: "kafka-shared-kafka-bootstrap.kafka.svc.cluster.local:9093"
features:
strimzi: true
tag: latest
serviceAccount:
annotations: {}
kacl:
belongsTo: shared
cluster: kafka-bootstrap.kafka.svc.cluster.local
tenant: vote
# capability user name in full username vote-api-user
user: demo
idempotent: false
global:
acls:
- topic: demo.team.red
role: writer
user: api
- topic: demo.team.green
role: writer
user: api
- topic: demo.team.blue
role: writer
user: api
metadata: {}
So we have grant literal write role to x3 topics . this can be dome with prefixed single entry as example :
global:
acls:
- topic: demo.team.
role: multiwriter
user: api
Create kacl deployment for user api . It provide default rights for vote-api-user to dev.vote.api. topics
belongsTo: shared
cluster: kafka-bootstrap.kafka.svc.cluster.local
tenant: vote
user: api
idempotent: false
acls: {}
global: {}
metadata: {}
The debug demo app has buil din deployment variable for SASL injection from secret that is auto created by kacl deployment. same for API application
- name: KAFKA_JAAS_CONFIG
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: sview-kafka-{{ $stage }}-{{.Values.kacl.tenant }}-{{ .Values.kacl.user }}-user
key: sasl.jaas.config
¶ Deploy Kafka as application
The Sview Kafka Topics Management Application is designed to manage Kafka topics within a single Kafka cluster. It allows users to define and manage an unlimited number of topics efficiently. The following steps outline the deployment process. Figure 1 .
Figure 1. Kafka Topics deployment
¶ Selections in deployment
- Prerequisite - Kafka cluster deployed
- From product catalog select your environment where you like to deploy it (1.1) .
- Select Kafka Topics application (1.2) and select/enter service (1.3) which is group of your applications.
- Enter namespace where kafka cluster is deployed as example kafka (1.4)
- Enter deployment name (1.5) <-- NOTE that it should match your kafka cluster deployment name
- Enter topics and topic configuration you like to auto create. Etch topic_name will be syncronised back to kafka cluster. If you remove some topic from the list it will be deleted in kafka cluster.
Its not suported to adjust replica and partitions count. Topic recreation required! If you adjust values then you need to delete topic, it will be created with new values.
¶ Access Kafka
¶ Raise Access Request
As Kafka is shared service access request can be raised on any application.
Raise kafka role access request and get it approved.
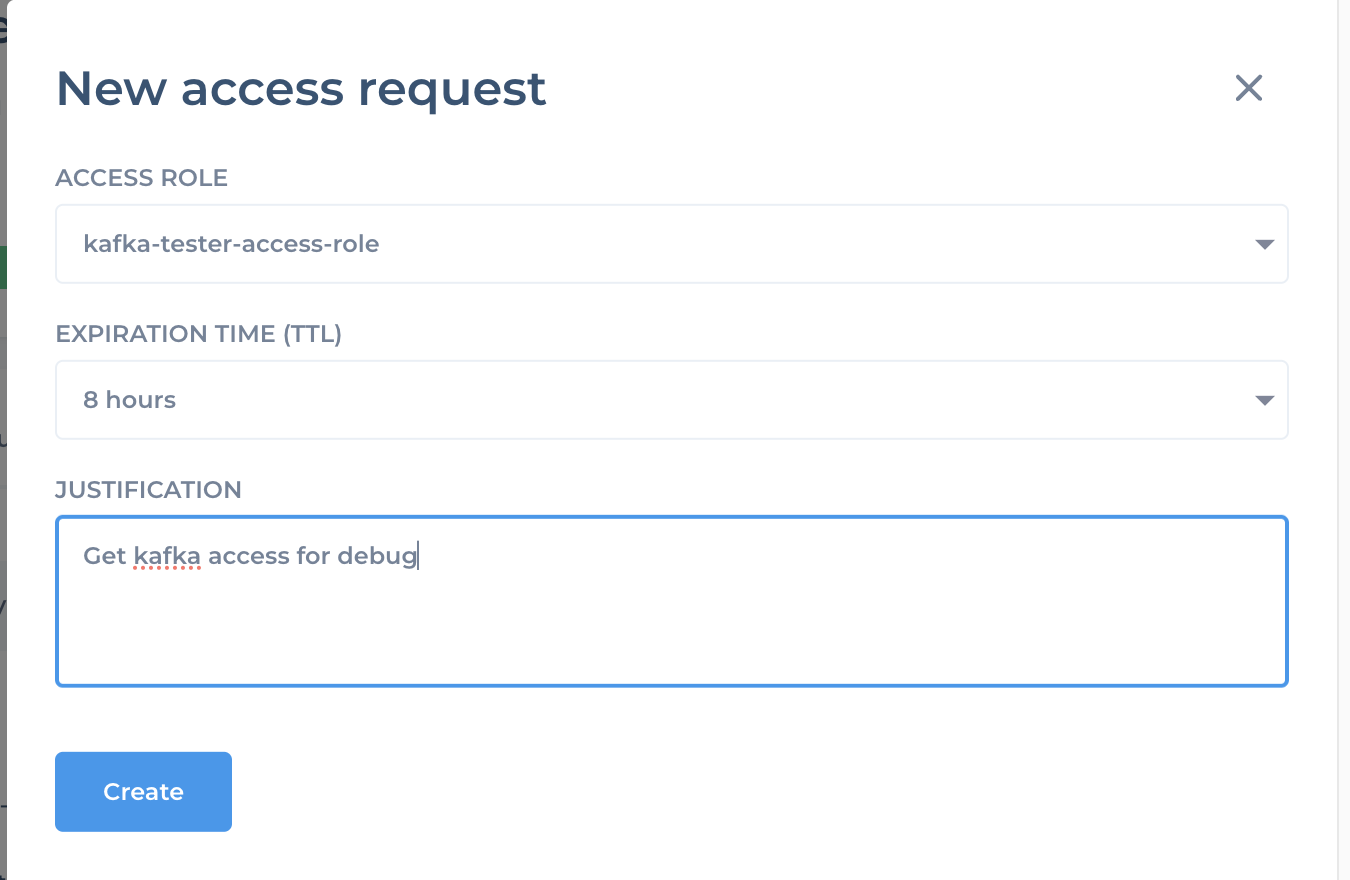
¶ One Time Actions
Below actions that needs to be done once per cluster
¶ Get SSL Certificate
To connect to Kafka SASL cluster you need transport encryption certificate. Etch kafka access role has namespace where kafka-debug pod and Certificate is located. Export certificate by running command
kubectl get secret kafka-acl-cert-role -n tester -o jsonpath='{.data.ca\.crt}'|base64 -d > ~/devstuff/myjavaapp/ca.crt
if you need import certificate to your application truststore run
keytool -importcert -alias kafka-ca -keystore /tmp/truststore.jks -storepass $TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD -file ~/devstuff/myjavaapp/ca.crt --noprompt
¶ Get SASL Jaas file
kubectl get secret sview-kafka-dev-multiadmin-tester-user -n tester -o jsonpath='{.data.sasl\.jaas\.config}'| base64 -d > ~/destuff/myjavaapp/user_jaas.conf
¶ PortForward
¶ Access Kafka
Once port forward is active. You can access kafka from your local comuper in localhost port 9093
¶ Prerequisite
update /etc/hosts file
127.0.0.1 kafka-shared-kafka-bootstrap.kafka.svc
127.0.0.2 kafka-shared-broker-0.kafka-shared-kafka-brokers.kafka.svc
127.0.0.3 kafka-shared-broker-1.kafka-shared-kafka-brokers.kafka.svc
127.0.0.4 kafka-shared-broker-2.kafka-shared-kafka-brokers.kafka.svc
add if virtual loopback interfaces to your PC
MacOS
sudo ifconfig lo0 alias 127.0.0.2 up
sudo ifconfig lo0 alias 127.0.0.3 up
sudo ifconfig lo0 alias 127.0.0.4 up
Linux
sudo ifconfig lo0 alias 127.0.0.* up
- Port forward additionaly every broker pod (you need multi sessions in Iterm )
kubectl port-forward --address 127.0.0.2 kafka-shared-broker-0 -n kafka 9093:9093
Forwarding from 127.0.0.2:9093 -> 9093
kubectl port-forward --address 127.0.0.3 kafka-shared-broker-1 -n kafka 9093:9093
Forwarding from 127.0.0.3:9093 -> 9093
kubectl port-forward --address 127.0.0.4 kafka-shared-broker-2 -n kafka 9093:9093
Forwarding from 127.0.0.4:9093 -> 9093
Or use k9s
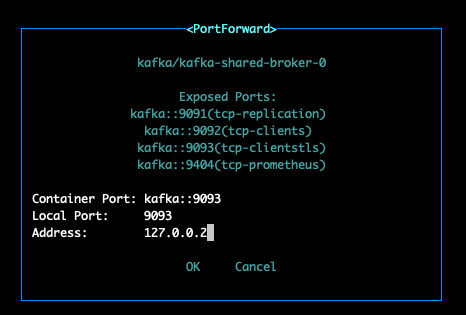

- port forward main bootsrap service
$ kubectl port-forward svc/kafka-shared-kafka-bootstrap -n kafka 9093:9093
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:9093 -> 9093
Forwarding from [::1]:9093 -> 9093
Now you can access
- access with your app or https://kafka.apache.org/downloads
export KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS=127.0.0.1:9093
export KAFKA_OPTS="-Djava.security.auth.login.config=/apps/tmp/user_jaas.conf"
cat ../config/client_sasl.properties
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-512
ssl.truststore.location=/tmp/truststore.jks
ssl.truststore.password=myjkspassword2334455
./kafka-topics.sh --list --bootstrap-server $KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS --command-config ../config/client_sasl.properties
¶ Access Kafka via debug pod
exec to kafka debug pod
kubectl get po -n tester
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kafka-debug-role-ffd54c746-r652j 1/1 Running 0 78m
kubectl exec -it kafka-debug-role-ffd54c746-r652j -n tester -c kafka-debug -- /bin/bash
bash-5.1# ./kafka_debug.sh -a -g
Sasl: 1
Starting debug in kafka-shared-kafka-bootstrap.kafka.svc.cluster.local:9093 | Output file: /tmp/kafka_debug_log.txt
###################### Getting all Kafka topics... ###################
...
./kafka-topics.sh --list --bootstrap-server $KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS --command-config ../config/client_sasl.properties
dev.demo.tst
dev.demo.sview
...